Did you know that 8 out of every 10 individuals assigned male at birth (AMAB) will get an enlarged prostate? This fact shows how common prostate issues are for men as they get older. By 60, there’s a 50% chance of noticing symptoms. And by 80, this risk goes up to 90%.
It’s crucial to know about prostate health and treatments to improve life quality for older men.
This article will explore prostate gland problems, from discomfort to serious issues like cancer. We’ll look at symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. This way, men can make informed decisions about their health.
Key Takeaways
- Around 8 in 10 AMAB individuals will develop prostate enlargement.
- 50% of men aged 60 experience symptoms related to prostate enlargement.
- Chronic prostatitis affects about 1 in 3 individuals AMAB at some point.
- Various treatment options exist, including medications and surgery.
- Screening for prostate cancer is essential, especially for those at higher risk.
- Understanding family history and lifestyle factors can aid in prevention.
What is the Prostate Gland?
The prostate gland is a small but key part of the male body. It sits below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds a part of the urethra. This gland is important for making semen, the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation.
Knowing about the prostate’s size is important. In young men, it’s about the size of a walnut. As men get older, it grows, reaching lemon size by age 60. This growth can lead to health problems, especially in older men.
- Normal prostate size in 20s: Walnut, approximately 2 cm
- Prostate size in 40s: Slight increase, approximately 3 cm
- Prostate size in 60s: Lemon-sized, approximately 4 cm
The prostate’s growth and function are key to health. Issues like prostatitis or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can arise. Knowing about the prostate helps spot health problems early and get the right treatment.
Common Prostate Gland Problems
Many men face prostate gland problems, especially as they get older. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue. It’s when the prostate grows too big but isn’t cancerous. It mainly hits men over 50, with about 70% of those in their sixties showing symptoms.
Symptoms include needing to pee a lot, weak urine flow, and sometimes not being able to hold it. Prostate disorder symptoms can really affect a man’s life.
Getting older is a big risk factor for BPH. Family history also plays a part, showing it might run in families. How active you are can also impact your risk. If BPH gets worse, it can cause serious problems like not being able to pee at all, infections, and harm to the bladder and kidneys.
Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate, is another big issue. It causes pain and makes it hard to pee. And then there’s prostate cancer, a big worry for older men. Knowing about common prostate gland problems and their symptoms is key. Regular check-ups and early action can help keep the prostate healthy, especially for older men.
Prostate Gland Problems: Symptoms to Watch For
Knowing the signs of prostate issues is key. Many men face symptoms that point to prostate problems. One common sign is needing to urinate often. This can make everyday tasks hard.
It’s also common to struggle with starting or stopping urination. Pain while urinating means there might be inflammation or infection. Seeing blood in urine or semen is a serious sign that needs quick doctor’s care.
Painful ejaculation or a weak urine stream are big red flags. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) causes long-lasting pain in the pelvic area. This pain often means there’s a prostate issue.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is rare but serious. It causes cloudy urine, high fever, and a strong urge to urinate. Chronic bacterial prostatitis lasts longer and causes ongoing pain and discomfort.
Knowing these symptoms is crucial for early detection. Treating these signs early can greatly improve life quality for those affected.
Diagnosing Prostate Gland Issues
Diagnosing prostate gland issues starts with a detailed patient history and physical exam. A digital rectal exam (DRE) is often used. It helps doctors check the prostate’s size and feel. This is key in diagnosing prostate problems.
Physical Examinations and Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
The DRE is a crucial first step. It helps find potential issues like benign prostatic hyperplasia or prostate cancer. Doctors use it to get a quick look at the prostate’s health. But, they usually do more tests after this.
Blood Tests and PSA Levels
Blood tests are important in diagnosing prostate issues. The PSA test checks for prostate-specific antigen levels. A PSA level of 4 ng/mL is seen as normal. But, levels over 10 ng/mL might mean a higher risk of prostate cancer.
Urinalysis and Imaging Techniques
Urinalysis helps find urinary tract infections or other prostate-related issues. Imaging, like ultrasounds, gives doctors a visual look. These diagnostic tests for prostate problems give a full picture of prostate health. They help decide what to do next.
Treatment for Prostate Gland Problems
Treatment for prostate gland problems varies based on the condition and its severity. It often includes medications, home remedies, and sometimes surgery. It’s important to consider each person’s situation to create an effective prostate gland dysfunction management plan.
Medications and Home Remedies
Medications are key in treating prostate issues. Alpha-blockers help by relaxing muscles around the prostate and bladder. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors also reduce prostate size, making it easier to urinate.
Home remedies can also help. Here are some suggestions:
- Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Do light exercise that fits your fitness level.
- Avoid foods that irritate the bladder, like caffeine and spicy foods.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers to manage symptoms.
Surgical Options for Severe Conditions
If medications don’t work or if the condition is severe, surgery might be needed. For localized prostate cancer, removing the prostate gland and surrounding tissue is an option. This is considered when the cancer hasn’t spread far.
For BPH complications, a procedure called transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) can help. It removes part of the prostate to ease urinary issues.
It’s crucial to have a treatment plan tailored to each person. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are important. They help ensure the right care is given based on individual health needs.
Understanding Prostatitis and Its Impact on Prostate Health
Prostatitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the prostate gland. It comes in several forms, making it key to know the different types. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is the most common, affecting many men’s lives.
This condition is the main cause of prostatitis. It can cause persistent pain in different parts of the body.
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of prostatitis, as they vary by type. Acute bacterial prostatitis shows with high fever and severe body aches. Chronic bacterial prostatitis may cause painful ejaculation and lower abdominal pain.
CPPS is known for its wide range of pains, making diagnosis and treatment harder.
Managing prostatitis involves a careful treatment plan. This includes lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Regular exercise, dietary changes, and sitz baths can help symptoms. For bacterial prostatitis, fluoroquinolones are often the first choice of antibiotics.
Seeking medical help quickly is crucial. It helps avoid serious issues like bacterial infections or prostatic abscesses.
Prostatitis is a common problem, leading to about 2 million outpatient visits in the U.S. each year. Up to 5% of men aged 20 to 50 may have chronic prostatitis. This can greatly reduce their quality of life, similar to serious health issues like ischemic heart disease.
Awareness of prostatitis’ impact is key for timely management and better outcomes.
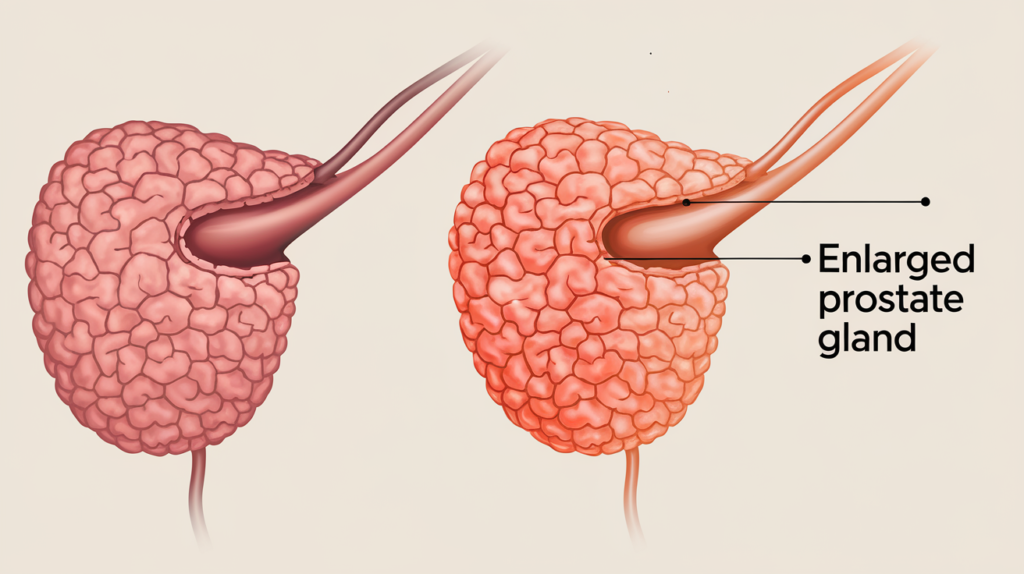
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Explained
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous growth of the prostate gland. It mainly affects older men. Over half of men aged 50 and older show signs of it. By 70, nearly 80% of men have BPH symptoms.
It’s important to know the symptoms and complications of BPH. This helps in managing this common condition.
Symptoms and Complications of BPH
The symptoms of BPH mainly affect urination. They include:
- Increased frequency of urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Straining to urinate
- A sensation of incomplete bladder emptying
BPH itself doesn’t cause prostate cancer. But, ignoring it can lead to complications. These can be urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or kidney damage. Knowing these symptoms helps in knowing when to see a doctor.
Treatment Options for BPH
Managing BPH depends on how bad the symptoms are. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating right, losing weight, and drinking more water.
- Medications: Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can help.
- Surgical Options: For severe symptoms, TURP or prostate artery embolization might be needed.
Prostate Cancer: Risk Factors and Symptoms
Prostate cancer is a big worry for men over 65. The prostate cancer risk factors include age, race, and family history. African American and Caribbean men of African ancestry have higher rates, showing why it’s key to know these factors.
Early Detection and Screening Methods
Screening early is vital in catching prostate cancer. Tests like PSA and Digital Rectal Exams (DREs) are key. Symptoms like trouble urinating or pain often show up late, making screenings crucial.
Treatment Strategies for Prostate Cancer
For prostate cancer treatment strategies, the choice depends on the cancer’s stage. Options include:
- Active surveillance for low-risk cases
- Surgery, like prostatectomy, for localized cancer
- Radiation therapy for both localized and advanced stages
- Hormone therapy to control cancer growth
Knowing about these treatments and their side effects helps patients choose wisely. By understanding prostate cancer risk factors and treatment options, people can manage their prostate health better.
| Risk Factor | Influence on Prostate Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
| Age | Increased risk as age advances, especially over 65 |
| Race | Higher incidence in African American and Caribbean men |
| Family History | More than double the risk with a close relative diagnosed |
| Obesity | No clear link to increased prostate cancer risk |
| Dairy Consumption | Slightly higher chance associated with high dairy intake |
| Environmental Exposures | Chemicals like arsenic linked to increased risk |
| Genetic Factors | Up to 10% of cases related to inherited gene changes |
Conclusion
Prostate gland problems are common among men, especially as they get older. By 60, about 50% of men have an enlarged prostate. This number jumps to 90% for those 85 and older.
It’s important to know the symptoms to manage prostate health well. Men should take care of their health by getting regular check-ups. This includes PSA blood tests and digital rectal exams, especially if there’s a family history of prostate issues.
Knowing about prostate health can help avoid problems like Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. While not all men with BPH show symptoms, ignoring it can cause serious issues. These include urinary tract infections, blockages, and kidney damage.
So, staying informed and talking to doctors about symptoms is key. This can greatly improve health outcomes and quality of life.
In short, learning more and talking to doctors is crucial for managing prostate problems. A healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and open discussions about health can help. This way, men can reduce risks and keep their prostate health in check as they age.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of prostate gland problems?
How is prostate gland dysfunction diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for prostate gland problems?
What is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
What is prostatitis, and how is it managed?
When should men start getting screened for prostate cancer?
Are there lifestyle changes that can help maintain prostate health?
What are the risk factors for developing prostate cancer?
Source Links
- What Is the Prostate? What’s Normal as You Age? – https://www.webmd.com/men/prostate-enlargement-bph/what-is-the-prostate
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – StatPearls – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558920/
- Prostate Diseases | Prostatitis | Enlarged Prostate | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/prostatediseases.html
- Understanding Prostate Changes – https://www.cancer.gov/types/prostate/understanding-prostate-changes
- Prostate cancer – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20353087
- Enlarged Prostate | BPH | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/enlargedprostatebph.html
- Enlarged Prostate (BPH) – https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/bph
- What Is Prostatitis? – https://www.webmd.com/men/prostatitis
- Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate | Georgia Prostate Institute – https://www.gaprostate.com/bph-symptoms/
- Tests for Prostate Cancer | Prostate Cancer Diagnosis – https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/how-diagnosed.html
- What Are the Warning Signs of Enlarged Prostate? – https://www.houstonmethodist.org/blog/articles/2024/feb/what-are-the-warning-signs-of-enlarged-prostate/
- Prostate cancer – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353093
- What Is Prostatitis? – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15319-prostatitis
- Chronic Prostatitis and Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome in Men – StatPearls – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK599550/
- BPH vs. Prostate Cancer: What’s the Difference? – https://www.webmd.com/prostate-cancer/bph-vs-prostate-cancer
- Surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/surgical-treatment-of-benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-bph
- What is BPH? | Georgia Prostate Institute – https://www.gaprostate.com/what-is-bph/
- Prostate Cancer Risk Factors | Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer – https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
- What Causes Prostate Cancer? – https://www.webmd.com/prostate-cancer/what-causes-prostate-cancer
- Prostate Cancer | Prostate Cancer Symptoms | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/prostatecancer.html
- Is An Enlarged Prostate Dangerous? What You Need To Know: Midwest Institute for Non-Surgical Therapy: Vascular and Interventional Radiologists – https://www.mintstl.com/blog/is-an-enlarged-prostate-dangerous-what-you-need-to-know
- If You Have Prostate Cancer | Prostate Cancer Guide – https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/if-you-have-prostate-cancer.html
- What causes prostate problems? – https://continentalhospitals.com/blog/what-causes-prostate-problems/








